Measure and get position on view react-native
Hi Guys, In this article, we are going to learn about how to get a view position in react-native, we are going to explore how to measure and get the position of react-native elements on the screen, we are going to use onLayout, measureInWindow, also displayed when view renders using onLayout and display onPress using measureInWindow, so let’s start
1. Create a new project
react-native init projectName
2. Imports following components
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View,FlatList, Button, ScrollView} from 'react-native';
3. Define default values in the constructor
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
scrollToHeight: 0,
vheight: 0,
vwidth: 0,
vpx:0,
vpy:0,
vfx:0,
vfy:0,
vx:0,
vy:0,
nativeEvent:null,
}
}
4. Measure view position onPress
We are using measureInWindow to measure the component position.
measure(){
this.refs.Marker.measureInWindow((x, y, width, height) => {
console.log("++++++ measureInWindow "+width+" "+height+" "+x+" "+y);
this.setState({ vheight: height, vwidth: width, vx: x, vy: y });
}
);
};
as you saw in the above method you are storing x, y position, and height, width in the state.
In the above method, we are using the view using reference this.refs.Marker just add ref=”Marker” in view which you want to measure like below
<View ref="Marker" />
5. Measure position using onLayout onRender view
You have to add onLayout on view like below.
<View
ref="Marker"
onLayout={({nativeEvent}) => {
this.setState({nativeEvent: nativeEvent.layout});
}}
>
// Add component
</View>
onLayout returns following JSON object using nativeEvent.layout
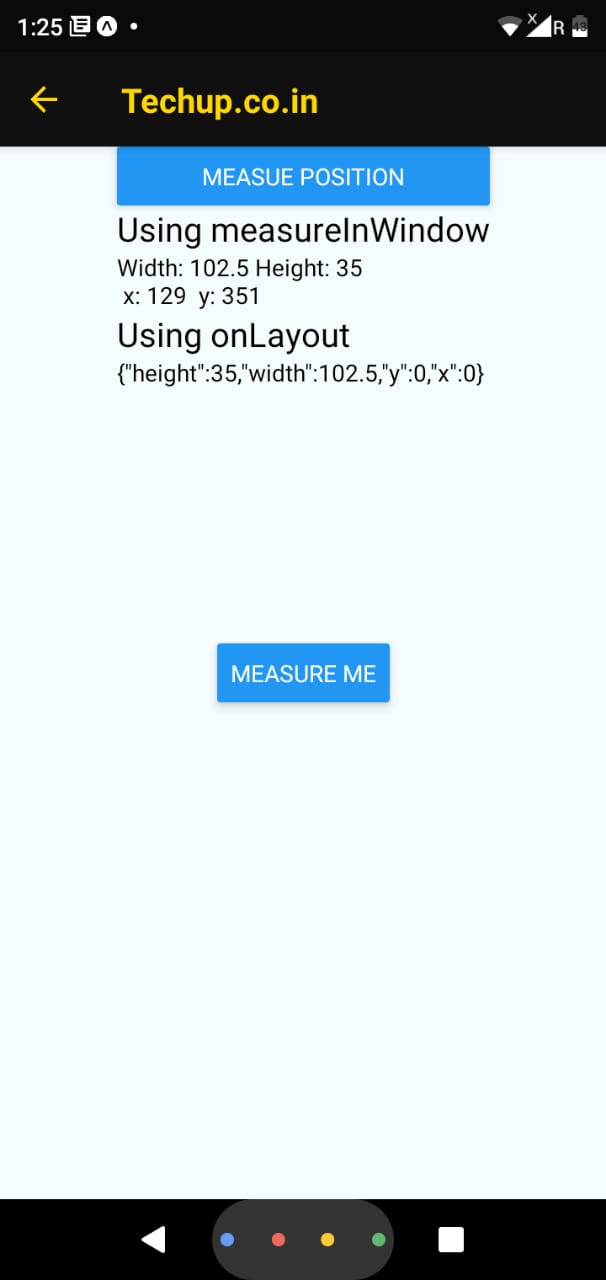
{"height": 35,"width":102.5,"y":0,"x":0}
Let’s see the full source code
6. Full source code
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View,FlatList, Button, ScrollView} from 'react-native';
//Define a color for toolbar
global.backgroundColor = '#176abf';
export default class Home extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
scrollToHeight: 0,
vheight: 0,
vwidth: 0,
vpx:0,
vpy:0,
vfx:0,
vfy:0,
vx:0,
vy:0,
nativeEvent:null,
}
}
static navigationOptions = ({ navigation }) => {
const { params } = navigation.state;
return {
title: 'Techup.co.in',
headerStyle: {
backgroundColor: '#000000',
},
headerTintColor: '##EED92B',
headerTitleStyle: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
}
};
componentDidMount() {
// do API call here
}
measure(){
this.refs.Marker.measureInWindow((x, y, width, height) => {
console.log("++++++ measureInWindow "+width+" "+height+" "+x+" "+y);
this.setState({ vheight: height, vwidth: width, vx: x, vy: y });
}
);
};
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View style={{flex:1}} >
<Button
title="Measue position"
onPress={() => this.measure()} // <---- Method called for measure position
/>
<Text style={{fontSize:20}}>Using measureInWindow</Text>
<Text>Width: {this.state.vwidth} Height: {this.state.vheight} {'\n'} x: {this.state.vx} y: {this.state.vy}</Text>
<Text style={{fontSize:20}}>Using onLayout</Text>
<Text>{ JSON.stringify(this.state.nativeEvent)}</Text>
</View>
<View >
<View style={{margin:10, alignItems:'center', justifyContent:'center'}}>
//We are going to measure position for this view
<View
ref="Marker"
onLayout={({nativeEvent}) => {
this.setState({nativeEvent: nativeEvent.layout});
}}
>
<Button
title="Measure me"
/>
</View>
</View>
</View>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
},
welcome: {
fontSize: 40,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10,
},
instructions: {
textAlign: 'center',
color: '#333333',
marginBottom: 5,
fontSize: 18,
},
});
7. Output:
Thank you 🙂





Awesome post.
Thank you